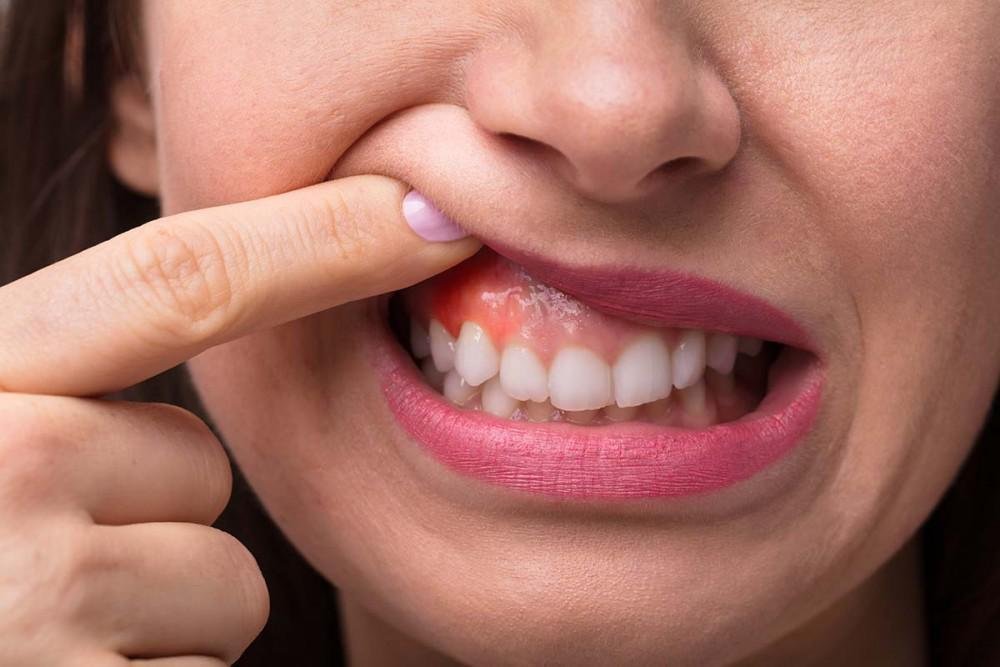
Gingivitis is one of the most common—but often overlooked—oral health issues. It’s the early stage of gum disease and is usually reversible if addressed promptly. Left untreated, however, it can progress to more severe periodontal disease, leading to tooth loss and other complications. In this guide, we’ll explore the causes, warning signs, and proven ways to treat and prevent gingivitis naturally.
What Is Gingivitis?

Gingivitis is the inflammation of the gums caused by bacterial plaque buildup along the gumline. While it’s typically painless in the early stages, signs such as bleeding when brushing or flossing should not be ignored. Gingivitis is reversible with proper oral care and lifestyle changes.
Common Causes of Gingivitis
- Poor oral hygiene habits
- Smoking or tobacco use
- Hormonal changes (pregnancy, puberty, menopause)
- Certain medications that reduce saliva flow
- Chronic health conditions like diabetes
- Vitamin deficiencies, particularly vitamin C
Symptoms to Watch For
- Red, swollen, or tender gums
- Bleeding while brushing or flossing
- Persistent bad breath
- Receding gums
- Soft or puffy gum tissue
How to Reverse Gingivitis Naturally
- Improve Brushing and Flossing Techniques: Brush twice a day with a soft-bristled toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste. Floss daily to remove plaque between teeth.
- Use Antibacterial Mouthwash: Rinsing helps reduce bacteria and inflammation.
- Eat a Nutrient-Dense Diet: Focus on foods high in vitamin C, antioxidants, and anti-inflammatory properties.
- Quit Smoking: Smoking limits healing and increases plaque buildup.
- Consider Oral Probiotics: Probiotic supplements like ProDentim may help restore healthy oral bacteria and reduce inflammation.
Preventing Gingivitis Long-Term
Prevention starts with consistency. Schedule regular dental cleanings, stay hydrated, maintain a balanced diet, and use natural oral health products when possible. Probiotic support can also help rebalance your oral microbiome, making your gums more resilient.
Next: The Link Between Gum Disease and Overall Health: What You Need to Know